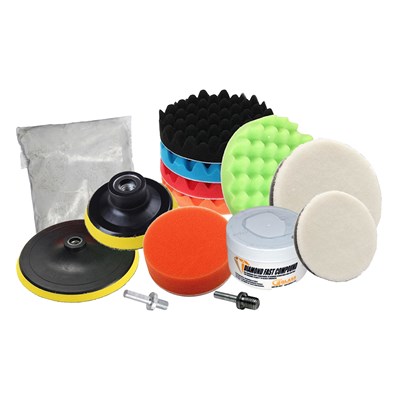
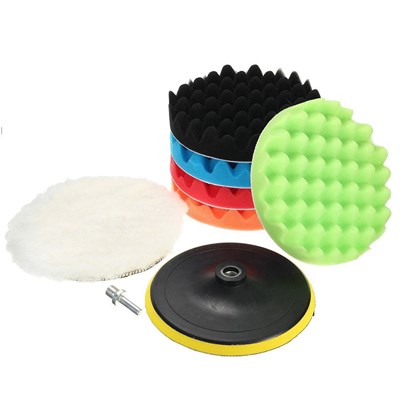
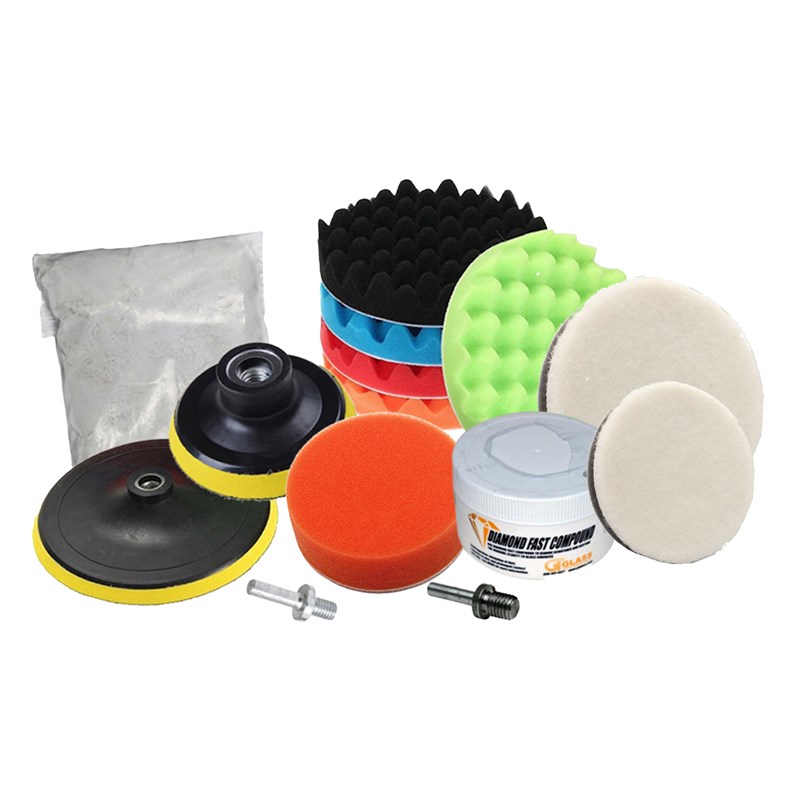
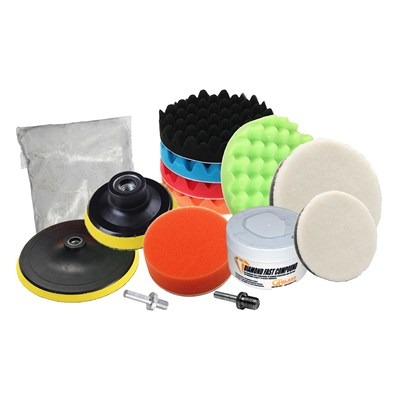
Polishing Kit, for glass, paint, granite remove stains and light scratches
Quick Overview
- This kit uses polishing pads and Cerium Oxide polish to polish away stains, lights scratches and rub marks from the surface
- Start with the Felt Pads and then use the Foam Polish Pads to create a high shine on your glass, auto paint and natural stone surfaces
- This Kit incudes the pads and adapters needed to remove scratches and poish the surface
- Foam and Felt Polishing Pad(s) are used to polish glass using Cerium Oxide, use the smaller pads in tight spaces and on headlamps
Show More
Polishing Kit, for glass, paint, granite remove stains and light scratches
Glass Polishing Kit with Cerium Oxide and Polishing Pads
Restoring and Polishing Glass, auto Paint, headlamps, polisjhed stone can be accoplished with this ket, it is important to understand the polishing pads are simply carriers for your cerium oxide slurry. The Pads provide a rotating surface that holds the cerium oxide and provides the required friction between your surface and the cerium oxide slurry.
The Polishing Kit is designed to remove mild blemishes and light surface scratches as well as restore a high shine to the surface of all types of glass; auto glass, glass furniture, windows and doors as well as polished stone.
Note: Since water is used in conjunction with this product, do not use it on electronic devices such as a TVs or computer monitors.
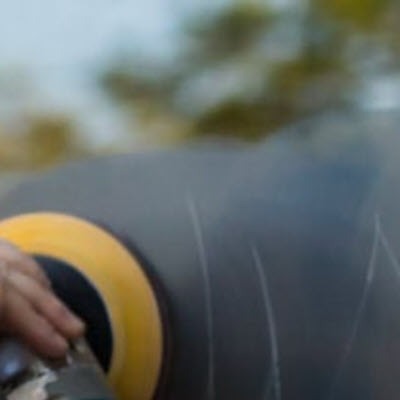
Cerium Oxide polishing is performed using a powered polisher or drill with a minimum operating speed of 1,500 rpm, hand polishing will not provide the same results.
To get the best results use a felt or foam polishing pad when applying the cerium oxide. It is also suggested to use a spray bottle filled with water to keep the area wet while polishing. Polishing creates heat which is the enemy of polishing, keep the surface wetted.
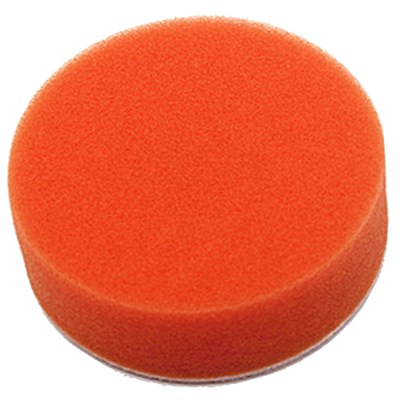
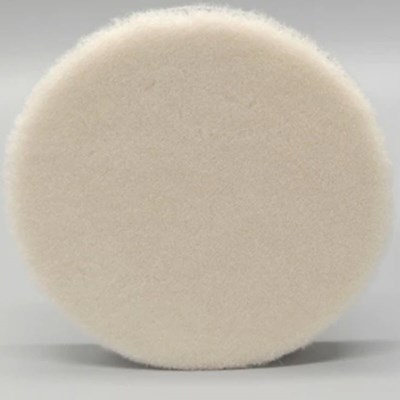
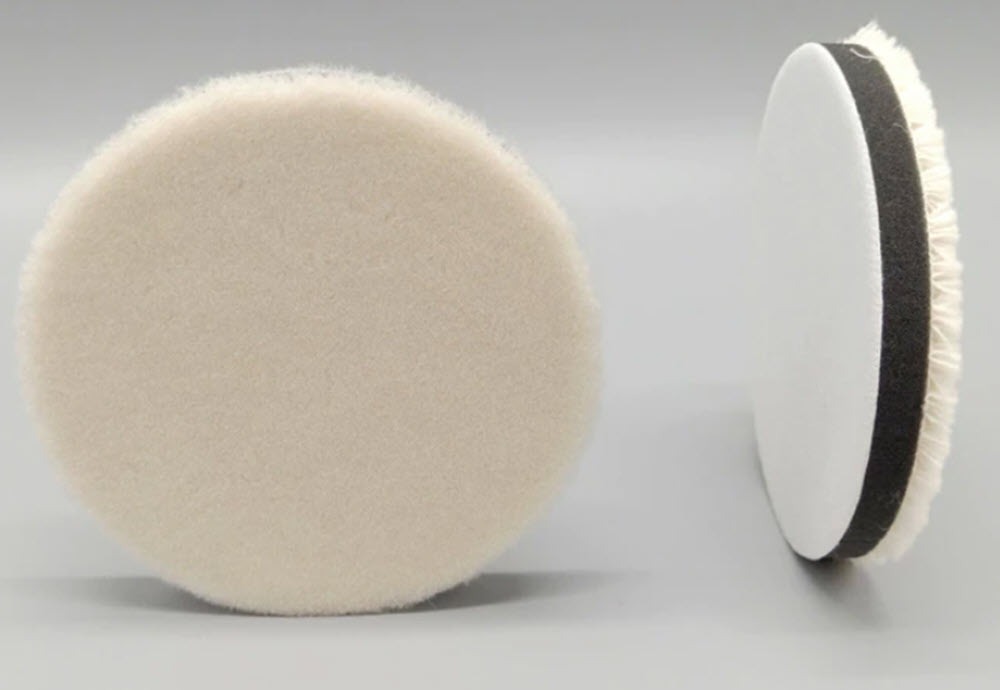
Foam Pads
Foam Pads are easier to use with the polisher as they have some "give" to them and are more gentle allowing the operator some leeway when holding the pad on the surface.
Foam pads can remove light scratches that are right on the surface by them selves, it just may take longer than starting with a Felt Pads.
Foam Pads will remove swirl marks and polishing streaks that were left behind by a Felt Pad. Foam Pads use less Cerium Oxide when polishing but generate heat faster than Felt.
The Flat Foam Pads retore the glass faster than "bumpy" Foam Pads, the bumpy pads generate as heat as quickly and are easier to use for a the final high shine polishing.


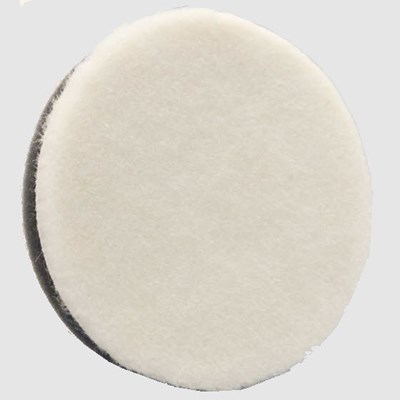
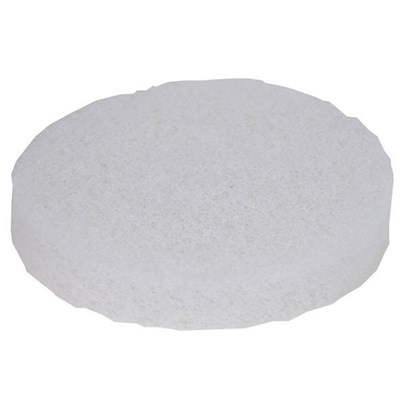
Felt Pads
Felt Pads are made from natural wool and are more abrasive than Foam Pads. When Felt Pads are used on painted surfaces they are referred to as "cutting pads" on Glass they will polish the surface faster. Felt pads are great for removing light scratches, Tin Etch Haze and Hard Water Stains faster than Foam Pads. Felt Pads will leave swirl trails on the surface, these can be polished out with the Foam Pads.
Target your pad rotational speed on Felt pads to around 1500 rpm
Start with Felt Pads when restoring the surface, moving to Foam Pads to finish the polishing.
Felt Pads also require more precise control of the rotating wheel and polisher.
Pad Size
The Larger Pads have more cutting power than the small pads, so if you are trying to remove heavy hard water deposits or haze the small pads may not work well. Choose a larger pad when the work is tough.
Small Pads are good for curved surfaces like the glass on some coach lamps, auto headlamps or paint. They also will get into corners better, always mask off the area that you do not want polished those adjoining surfaces that the pad may rub on.
Felt Pads require more Cerirum Oxide for the same surface area and Foam Pads and Felt Pads tend to through more splatter.
Felt Pads do not generate heat as quickly as Foam pads


The work area should be reviewd for areas where you do not want splatter to impact cleanup of stain the surface.
Mask the areas that are adjacent to the polishing area where you do not want the rotating pad to touch and potentially mar or damage the surface.
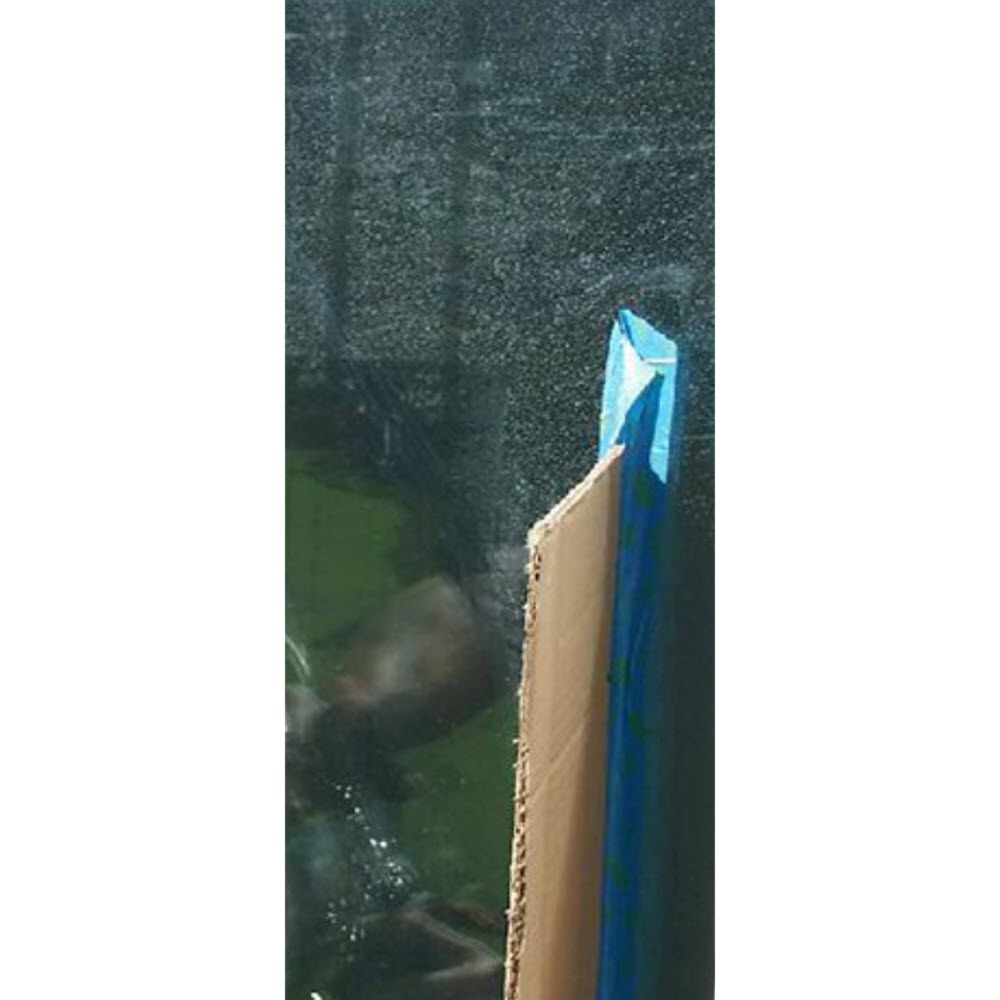


Splatter Dam
Created from Cardboard and Tape and dsigned to catch any slurry that spins off of the polish pad
-wo5kv3.jpg)
Protected Surface around Target Area
Apply protective tape to the surfaces where you do not want the Cerium Oxide to spraye or the polish pad to touch
-DYNoW4.jpg)
Protecting the Frame
Protect the frame from both from any bleaching/whitening effect from the Cerium Oxide as well as the buffing action of the rotating Polish Pad.
DIRECTIONS:
Start by thoroughly cleaning the surface of the glass to remove any dirt, debris, or contaminants from the surface of the glass.
It is best to use ammonia-free glass cleaner, isopropyl alcohol, or pure water to clean the glass.
Start by masking off the work area to protect any surrounding surfaces from exposure to water and cerium powder.
Powder vs Compound (Pre-Mix)
- For Larger Tasks the Powder will be the more economical than the Compound.
- The compound is ready to use and great for small restoration projects.
Powder Preperation
- Find the Cerium Oxide Powder Packet and pour 3 or 4 tablespoons onto a small plate or bowl.
- Add water to the plate/bowl until the powder changes to a paste-like consistency.
Polishing
- Apply a thin layer of cerium paste to the pad.
- Hold the pad flat to the glass, paint, stone and turn the power tool on.
- Go over the damaged area for several minutes adding water as needed to maintain a wet surface.
- When polish appears heavily diluted by the addition of water, stop and apply another layer of cerium paste to the pad. Don’t overuse cerium oxide, as too much cerium will act as a lubricant instead of a polish.
- Repeat the application of polish until the damaged area has been restored.
- Use water and/or glass cleaner to clean the glass and surrounding area immediately after you have finished restoring the glass.
Tip: If the Felt Pad builds up to much Cerium Oxide on the suface, you will want to remove the excess, use a plastic brush like a hair brush, or kitchen pot or pan brush, as a wire brush could leave a bit of wire bristle in the felt and cause damage to the surface you are working on.
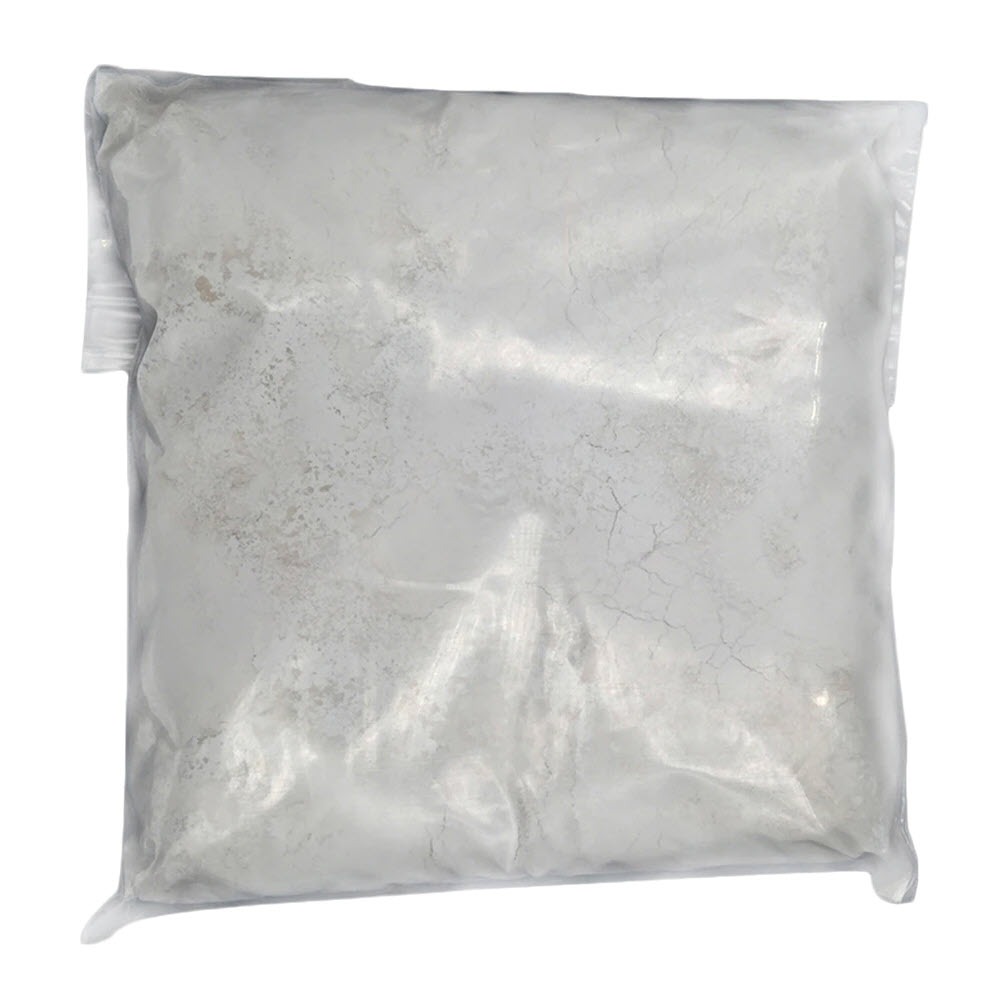



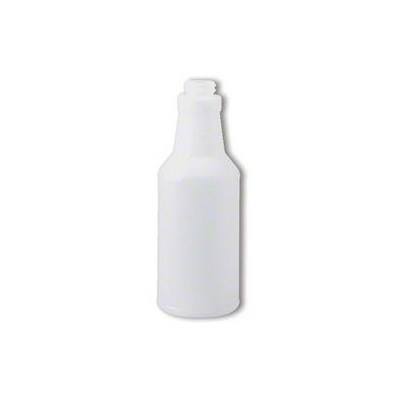
8 oz Bottle with Cerium Powder
In addition to the slurry mixture above, the Cerium Oxide can be perpared in the 8oz bottle in the kit and applied to the pad as a simple squeeze/squirt action.
This is usefull when you are working from a Ladder or suspended on a chair. Note: When on the Ladder we recommend using a Harness with a Front D Ring and the 3rd Hand Ladder Strap. Along with securing the ladder, perhaps with a Ladder Lock.
8 oz Bottle Mix water with the Cerium Oxide Powder in the small squirt bottle until it is a creamy liquid, then squirt small amounts in the center of your polishing pad as you work to achieve your polish. Use just enough water with the cerium powder to keep your pad moist as you work so you don’t burn the cerium onto your glass. Don’t overuse cerium oxide, as too much cerium will act as a lubricant instead of a polish.

Proposition 65 requires businesses to provide warnings to Californians about significant exposures to chemicals that cause cancer, birth defects or other reproductive harm. These chemicals can be in the products that Californians purchase, in their homes or workplaces, or that are released into the environment. By requiring that this information be provided, Proposition 65 enables Californians to make informed decisions about their exposures to these chemicals. Proposition 65 also prohibits California businesses from knowingly discharging significant amounts of listed chemicals into sources of drinking water. Proposition 65 requires California to publish a list of chemicals known to cause cancer, birth defects or other reproductive harm. This list, which must be updated at least once a year, has grown to include approximately 900 chemicals since it was first published in 1987. Proposition 65 became law in November 1986, when California voters approved it by a 63-37 percent margin. The official name of Proposition 65 is the Safe Drinking Water and Toxic Enforcement Act of 1986.
The list of chemicals contains a wide range of naturally occurring and synthetic chemicals that include additives or ingredients in pesticides, common household products, food, drugs, dyes, or solvents. Listed chemicals may also be used in manufacturing and construction, or they may be byproducts of chemical processes, such as motor vehicle exhaust. For more information visit www.p65warnings.ca.gov/