Detailed Guide: Wiring Pumps Through a Bus Bar and Circuit Breaker
Detailed Guide: Wiring Pumps Through a Bus Bar and Circuit Breaker
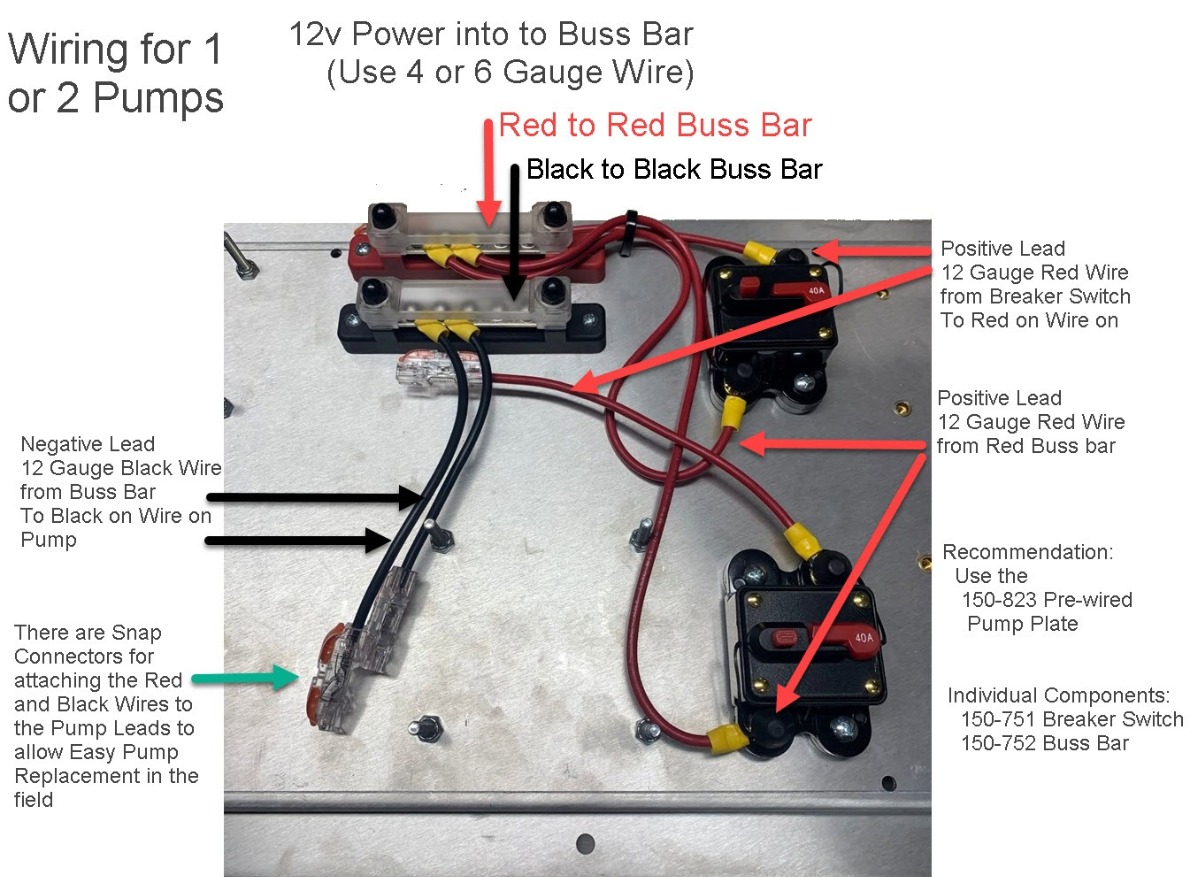
Detailed Guide: Wiring Pumps Through a Bus Bar and Circuit Breaker
Setting up a reliable and efficient electrical system for your pumps involves wiring through a bus bar and circuit breaker. This method not only ensures safety but also enhances the system's durability and manageability. Here’s a detailed guide on how to wire your pumps using a bus bar and circuit breaker, along with reasons why breakers are preferred over fuses.
Materials Needed:
- Bus bar
- Circuit breaker
- 4 to 6 gauge wire (from the 12V power source to the bus bar)
- 12 gauge wire (from the bus bar to the breaker and from the breaker to the pumps)
- Pumps
- Connectors and terminals
Steps:
Wiring from Power Source to Bus Bar:
Use 4 to 6 Gauge Wire:
- This thicker wire is necessary to handle the high current from the 12V power source to the bus bar, reducing voltage drop and preventing overheating.
Connect Red Wire:
- Run a red 4 to 6 gauge wire from the positive terminal of your 12V power source to the red bus bar. Ensure the connection is secure using appropriate connectors.
Connect Black Wire:
- Similarly, connect a black 4 to 6 gauge wire from the negative terminal of your power source to the black bus bar.
Wiring to the Circuit Breaker:
Use 12 Gauge Wire:
- This wire is suitable for handling the current to each pump through the circuit breaker.
Connect Red Wires to Breaker:
- From the red bus bar, run a 12 gauge red wire to the input terminal of the circuit breaker.
- From the output terminal of the circuit breaker, run another red 12 gauge wire to the positive terminal of the pump.
Connect Black Wires to Pump:
- Run a black 12 gauge wire from the black bus bar directly to the negative terminal of the pump.
Why Use Circuit Breakers Instead of Fuses:
Resettable Protection:
- Circuit breakers can be reset after tripping due to an overload or short circuit, whereas fuses need to be replaced every time they blow.
Enhanced Safety:
- Breakers provide more consistent protection and can be manually turned off for maintenance or emergency purposes.
Convenience:
- The ability to quickly reset a breaker without the need for spare fuses makes them more convenient and reduces downtime.
Reliability:
- Breakers offer reliable protection and are less likely to degrade over time compared to fuses.
Connection Overview:
Red Wires:
- Connect from the 12V power source to the red bus bar using 4 to 6 gauge wire.
- Run from the red bus bar to the circuit breaker input with 12 gauge wire.
- From the circuit breaker output, connect to the pump's positive terminal with 12 gauge wire.
Black Wires:
- Connect from the 12V power source to the black bus bar using 4 to 6 gauge wire.
- Run from the black bus bar directly to the pump's negative terminal with 12 gauge wire.
Conclusion
By following this setup, you ensure a robust, efficient, and safe electrical system for your pumps. Utilizing a bus bar simplifies wiring and management, while circuit breakers provide reliable and resettable protection, enhancing the overall durability and functionality of your setup. This method not only streamlines the wiring process but also ensures long-term reliability and safety for your pumping system.

